10 Best Digital Oscilloscopes 2026 in the United States
Our technology thoroughly searches through the online shopping world, reviewing hundreds of sites. We then process and analyze this information, updating in real-time to bring you the latest top-rated products. This way, you always get the best and most current options available.

Our Top Picks
Winner
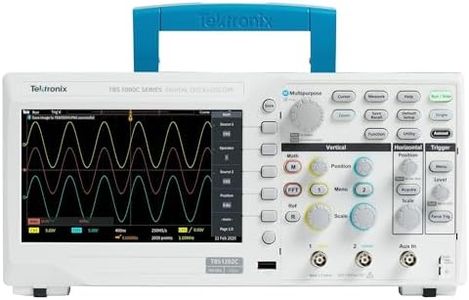
Tektronix TBS2204B 4-Ch Digital Storage Oscilloscope, 200 MHz, 2 GS/s
The Tektronix TBS2204B is a digital storage oscilloscope designed for users who require precision and versatility in their measurements. With a bandwidth of 200 MHz and a sampling rate of 2 GS/s, it offers a solid performance for a variety of electronic applications, making it suitable for both professionals and advanced hobbyists. The four analog channels allow users to observe multiple signals simultaneously, which is particularly beneficial when troubleshooting complex circuits.
One of the standout features is the 5 M record length on all channels, providing ample memory for capturing longer signal events. This is great for detailed analysis without missing crucial data. The 9-inch WVGA color display is another strong point, offering 50% more horizontal grids compared to many competitors, which enhances visibility and makes it easier to analyze waveforms clearly.
There are some drawbacks to consider. At 39.68 pounds, the oscilloscope is relatively heavy and might not be ideal for portable use or for those needing a device that can be easily transported. Additionally, while the specifications are impressive, beginners might find the professional-grade features overwhelming, as they require a certain level of expertise to fully utilize.
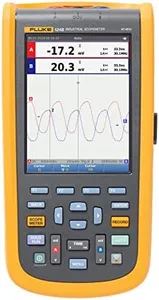
Fluke 123B Industrial ScopeMeter Hand-held Oscilloscope, 2 Input Channels, 20 MHZ Bandwidth, SCC120 Kit
Most important from
14 reviews
The Fluke 123B Industrial ScopeMeter is a sturdy and portable handheld oscilloscope designed mainly for industrial fieldwork. With two input channels and a 20 MHz bandwidth, it suits basic to moderate waveform analysis, especially for troubleshooting electrical signals in machinery and equipment. This model focuses on simplicity and durability rather than high-end lab capabilities. Its true-RMS digital multimeter functionality adds value by allowing precise voltage and current measurements alongside waveform capture.
The Connect-and-View and IntellaSet Auto Reading technologies help users quickly get accurate readings without deep oscilloscope expertise, which is excellent for technicians needing fast diagnostics. The seven-hour battery life with rechargeable Li-Ion battery is convenient for extended field use. The relatively low bandwidth means it might not meet demands for detailed signal analysis or complex triggering scenarios. The display details are minimal, likely adequate but not advanced.
Weighing just over 3 pounds and designed as a handheld unit, it’s portable but not pocket-sized. This device fits well for industrial technicians who prioritize ease of use, durability, and basic oscilloscope functions in the field, but it is less suitable for users needing high-speed sampling, deep memory, or advanced triggering features.
Most important from
14 reviews
Fluke 190-204/AM/S 4 Channel LCD Color ScopeMeter Oscilloscope with SCC290 Kit, 200 MHz Bandwidth, 1.7ns Rise time
Most important from
7 reviews
The Fluke 190-204/AM/S is a handheld digital oscilloscope with four channels and a 200 MHz bandwidth, making it suitable for professionals who need to capture and analyze multiple electrical signals simultaneously. Its real-time sample rate is 2.5 GS/s, which helps in accurately displaying fast-changing signals, and the memory depth of 10,000 points per channel allows detailed waveform recording. The 6-inch color LCD is large enough to view up to four waveforms or measurements at once, which is helpful for clear analysis on the go.
It also features handy tools like zoom, math functions including FFT for frequency analysis, and automatic measurements to simplify signal interpretation. Safety ratings for use in high-voltage environments (CAT III 1000V and CAT IV 600V) make it reliable for industrial settings. One thing to note is its weight—about 16 pounds—which is heavier than many portable scopes, so it might feel bulky during extended handheld use.
This oscilloscope represents a strong choice for technicians seeking a rugged, multi-channel instrument with good bandwidth and sample rate, especially when working in demanding environments.